What Is Muting In Safety?
Key Takeaway
Muting in safety refers to the temporary, automatic deactivation of electrosensitive protective equipment such as light barriers, light grids, light curtains, or laser scanners. This function is crucial during industrial processes where materials need to pass through a protected area without triggering a safety response. Muting ensures that machinery can continue operating without interruption while still maintaining safety measures. It is carefully controlled and only active during specific conditions to ensure that the safety of operators is not compromised. Once the condition for muting is cleared, the safety functions reactivate automatically, resuming full protection.
The Concept of Muting in Safety Systems
Muting is a feature in safety systems that temporarily overrides the safety response of devices like light curtains, allowing specific, predetermined operations to proceed without interruption. The primary purpose of muting is to enable the passage of materials or products through a safety zone without stopping machinery, which is essential in automated production lines. By distinguishing between safe and potentially hazardous interruptions, muting ensures that efficiency is maintained without compromising worker safety.
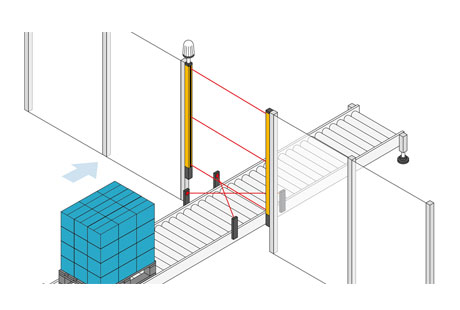
How Muting Enhances Machine Safety
Muting enhances machine safety by allowing for controlled exceptions to the standard safety protocols. In an automated environment, materials often need to move through protected areas. Without muting, every time an object crosses a light curtain, the machine would stop, causing significant delays. Muting allows these objects to pass through without halting the machine, ensuring continuous operation. This functionality is particularly beneficial in processes like packaging, assembly lines, and material handling, where frequent interruptions could severely impact productivity. By integrating muting, companies can achieve a safer and more efficient workflow.
Detailed Examination of Muting Mechanisms
Muting light curtain mechanisms rely on sophisticated sensors and control logic to ensure safe and efficient operation. Additional sensors are strategically placed before and after the light curtain. When these sensors detect an authorized object, the muting function is triggered. Here’s how the process unfolds:
- Detection: Sensors identify the authorized object approaching the safety zone.
- Activation: The muting function activates, allowing the light curtain to temporarily ignore the object’s interruption.
- Passage: The object passes through without halting machine operations.
- Deactivation: Once the object exits the safety zone, the muting function deactivates, restoring normal operation.
This sequence ensures that only specific, predefined objects can safely bypass the muting light curtain, maintaining safety and operational efficiency.
Step-by-Step Guide to Setting Up Muting Functions
Setting up muting functions involves several key steps to ensure both safety and functionality. Here’s a simplified guide:
Identify the Need: Determine where muting is necessary in your operation. Typical areas include conveyor belts and automated material handling systems.
Select Appropriate Sensors: Choose sensors that can reliably detect the authorized objects. These should be positioned to detect the object before it reaches the light curtain.
Configure the System: Program the safety system to recognize the sensor signals and activate the muting function accordingly.
Test the Setup: Conduct thorough testing to ensure that the muting function works correctly and does not compromise safety.
Implement Safety Standards: Ensure that the setup complies with relevant safety standards and regulations, and make any necessary adjustments based on the results of the testing phase.
Following these steps helps ensure that the muting function enhances safety and efficiency without introducing new risks.
Safety Standards Related to Muting
Muting functions must comply with various safety standards to ensure they are used correctly and effectively. Key standards include:
ISO 13849: This standard outlines the safety requirements for the design and integration of safety-related parts of control systems.
IEC 61496: This standard specifies the safety requirements for electro-sensitive protective equipment, including light curtains.
OSHA Regulations: Occupational Safety and Health Administration regulations may also apply, depending on the region and industry.
Compliance with these standards ensures that muting functions are implemented safely and legally, providing reliable protection for workers.
Conclusion
In conclusion, muting is a vital safety feature that significantly enhances both safety and efficiency in industrial operations. By allowing specific, authorized objects to bypass safety barriers without stopping machinery, muting helps maintain continuous workflow while ensuring the safety of workers. Understanding the concept, benefits, mechanisms, setup process, and safety standards related to muting is crucial for any industrial setting aiming to optimize their safety systems. Investing in proper muting functions not only safeguards employees but also boosts productivity, making it an indispensable part of modern industrial safety.
