Does An Ethernet Switch Need A Router?
Key Takeaway
An Ethernet switch does not need a router to function, but they serve different purposes. An Ethernet switch connects multiple devices within a local network, allowing them to communicate with each other. It is ideal for expanding the number of Ethernet ports in your network.
However, to access the internet, a router is necessary. The router connects your local network to the internet and assigns IP addresses to devices. While a switch manages local traffic, a router handles external connections. In homes and small offices, a router is essential for internet access, while a switch is useful if you need more Ethernet ports for additional devices.
Roles of Ethernet Switches and Routers in a Network
An Ethernet switch is a device that connects multiple devices within the same local area network (LAN). It operates at the data link layer (Layer 2) of the OSI model and uses MAC addresses to forward data to the correct destination. Switches help reduce network congestion by sending data only to the intended recipient, thereby improving overall network performance.
On the other hand, a router operates at the network layer (Layer 3) and is responsible for directing data between different networks. Routers use IP addresses to determine the best path for data to travel from one network to another, such as from a home network to the internet. They also provide essential services like DHCP (Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol) and NAT (Network Address Translation), which help manage and assign IP addresses within a network.
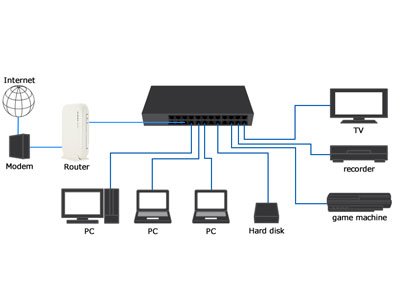
How Ethernet Switches and Routers Work Together
Ethernet switches and routers often work in tandem to create efficient and robust networks. In a typical home or small business setup, the router is the gateway to the internet. It connects to the internet service provider (ISP) and provides internet access to the network. The router also handles important functions like IP address assignment through DHCP and serves as the first line of defense with its built-in firewall.
On the other hand, Ethernet switches expand the local network by providing additional ports for connecting multiple devices. For example, in a home network, a router may only have four Ethernet ports. By connecting an Ethernet switch to one of these ports, you can significantly increase the number of devices that can be connected. Devices such as computers, printers, smart TVs, and gaming consoles can all connect to the switch. The router remains responsible for managing the IP addresses and routing traffic to and from the internet, while the switch efficiently handles internal data traffic. This setup ensures that devices can communicate with each other within the local network without overloading the router.
This collaboration between switches and routers is essential for maintaining a streamlined and high-performing network. The switch’s role in managing internal traffic reduces the burden on the router, allowing it to focus on its core functions of routing and security. By using both devices together, you achieve a balanced and efficient network that can handle both local and internet traffic seamlessly.
Network Scenarios: When to Use an Ethernet Switch Without a Router
While routers are a staple in most network setups, there are specific scenarios where an Ethernet switch can function effectively without a router. This is typically the case in closed networks where internet access is not required. For instance, in a small office or industrial setting, an Ethernet switch can connect all devices, enabling local file sharing, printer access, and other network services without needing a router. This setup simplifies the network by eliminating the need for IP address management and routing functions, which are not necessary when all communication is local.
Another scenario involves larger networks where multiple switches are used to connect various segments. In such environments, a central router might handle all external traffic, but the switches manage internal data flow. For example, in a large enterprise with multiple departments, each department might have its own managed Ethernet switch connecting computers, printers, and other devices. These switches communicate directly with each other to handle local traffic within the department, reducing the load on the central router and improving overall network efficiency. The router’s role is limited to managing traffic between different departments and providing internet access.
In these scenarios, switches are instrumental in managing and optimizing local network traffic. They ensure that data packets are forwarded efficiently to the intended recipients, minimizing delays and congestion. This setup is particularly beneficial in environments where high-speed, low-latency communication is critical, such as in industrial automation, where machinery and control systems need to communicate reliably and quickly. By understanding when and how to use Ethernet switches without routers, network administrators can design networks that meet specific operational needs while maintaining simplicity and efficiency.
Benefits of Combining Ethernet Switches and Routers
Combining Ethernet switches and routers in a network offers several significant benefits, making it a preferred setup for both small and large-scale networks. One of the primary advantages is scalability. Ethernet switches can expand the number of devices that connect to the network without overloading the router. This is particularly useful in growing networks where the demand for connectivity continuously increases. By distributing the network load across multiple switches, you can maintain optimal performance even as more devices join the network.
Additionally, this combination enhances network performance by efficiently managing traffic. Switches handle local data traffic, ensuring that internal communications are fast and reliable, while routers manage external communications, such as internet traffic. This division of labor prevents bottlenecks and ensures that data flows smoothly throughout the network.
Moreover, using both switches and routers improves overall network management. Routers provide advanced features like firewall protection, VPN support, and Quality of Service (QoS), which are crucial for securing and optimizing network traffic. QoS, for instance, allows you to prioritize certain types of traffic, ensuring that critical applications receive the necessary bandwidth. On the other hand, managed switches offer features like VLAN support and traffic monitoring, adding an extra layer of control and security to the network. VLANs can segment network traffic, enhancing security by isolating sensitive data and reducing broadcast traffic. Together, these devices create a robust and versatile network infrastructure that can handle a wide range of networking needs effectively.
Setting Up a Network with Ethernet Switches and Routers
Setting up a network with Ethernet switches and routers involves a few straightforward steps that ensure a stable and efficient network. Begin by connecting the router to your ISP’s modem to establish internet access. This router will serve as the central gateway for all external communications. Once the router is connected and configured, you can then extend the network by connecting an Ethernet switch to one of the router’s LAN ports. This setup allows additional devices to connect to the network via the switch, increasing the number of available ports without compromising performance.
Ensure that the router’s DHCP service is enabled. DHCP automatically assigns IP addresses to all connected devices, simplifying network management and ensuring each device can communicate effectively. This step is crucial for preventing IP conflicts and maintaining seamless connectivity across the network.
For more complex setups, particularly in larger networks or business environments, consider using managed switches. Managed switches can be configured to create VLANs, which segment the network into different sub-networks for improved security and traffic management. VLANs can isolate traffic from different departments or applications, reducing the risk of data breaches and optimizing bandwidth usage.
Conclusion
While an Ethernet switch does not strictly need a router, combining both devices creates a more efficient and versatile network. Routers handle external traffic and provide essential services like IP addressing, while switches manage internal data flow, enhancing network performance and scalability. Understanding the roles and benefits of each device helps in building robust and reliable networks tailored to specific needs. Whether for home, business, or industrial use, leveraging the strengths of Ethernet switches and routers ensures a smooth and efficient networking experience.
