How Does Solar Power Work?
Key Takeaway
Solar power works by converting sunlight into electricity using solar panels. These panels contain photovoltaic (PV) cells that absorb sunlight. When sunlight hits the PV cells, it creates electrical charges. These charges move due to an internal electrical field within the cells, generating a flow of electricity. This electricity can be used to power homes, businesses, and devices. Solar power is a clean, renewable energy source, reducing reliance on fossil fuels and lowering carbon emissions. Understanding solar power helps in appreciating its benefits and applications in sustainable energy solutions.
Basic Principles of Solar Energy
Solar energy harnesses the power of the sun to generate electricity. The sun emits an immense amount of energy in the form of light and heat, which can be converted into usable electricity using photovoltaic (PV) technology. Solar power systems capture sunlight through solar panels, which are made up of numerous solar cells. These cells contain semiconductor materials, typically silicon, that absorb photons from sunlight and release electrons. This process creates an electric current, which can be used to power homes, businesses, and various devices.
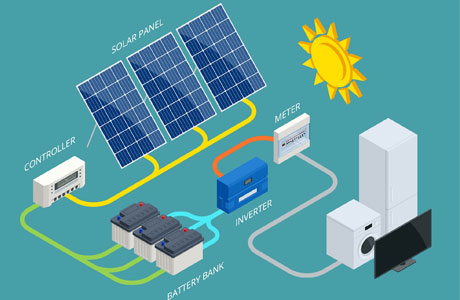
Components of a Solar Power System
A solar power system comprises essential components that work together to harness and convert sunlight into usable electricity. At the heart of this system are solar panels, equipped with photovoltaic cells that convert sunlight directly into electricity through the photovoltaic effect. These panels are typically installed on rooftops or open areas where they can capture maximum sunlight.
An integral part of the solar power setup is the inverter, which plays a crucial role in converting the direct current (DC) produced by the solar panels into alternating current (AC). AC is the standard form of electricity used by most household appliances and is compatible with the electrical grid, enabling seamless integration with existing power infrastructure.
To ensure the effective functioning of solar panels, mounting systems are employed to securely install and position them for optimal sunlight exposure. This positioning maximizes the efficiency of electricity generation throughout the day. Additionally, a monitoring system is employed to track the performance and efficiency of the solar power system. It provides real-time data on energy production, ensuring optimal operation and identifying any potential issues promptly.
For enhanced energy independence and reliability, some solar power systems include batteries for energy storage. These batteries store excess electricity generated during sunny periods for use during nighttime or cloudy days, thereby providing continuous power supply even when sunlight is unavailable.
Together, these components form a robust solar power system that offers sustainable and renewable energy solutions, reducing reliance on traditional fossil fuels and contributing to environmental conservation efforts.
How Solar Panels Convert Sunlight into Electricity
Solar panels harness the sun’s energy through a process known as the photovoltaic effect. This effect relies on semiconductor materials within the solar cells, typically made of silicon. When sunlight strikes these cells, it energizes the electrons within the semiconductor material, causing them to break free from their atoms and generate an electric current. This movement of electrons creates a flow of electricity, known as direct current (DC).
Each solar cell produces a small amount of DC electricity, but when numerous cells are interconnected within a panel, they collectively generate a substantial amount of power. These interconnected panels are designed to capture as much sunlight as possible throughout the day, maximizing energy production.
The generated DC electricity is then directed to an inverter, a critical component of the solar power system. The inverter converts the DC electricity into alternating current (AC), which is the standard form of electricity used in homes and businesses. AC electricity is compatible with the electrical grid and can power appliances, lighting, and other electrical devices seamlessly.
This conversion process is efficient and sustainable, offering a renewable energy solution that reduces reliance on non-renewable fossil fuels. Solar power systems contribute to environmental conservation efforts by harnessing clean energy from the sun, making them an increasingly popular choice for sustainable energy solutions worldwide, including in India.
Benefits and Drawbacks of Solar Power
Solar power presents several compelling benefits. Firstly, it is a renewable energy source, meaning it draws on an abundant and virtually inexhaustible resource: sunlight. By harnessing solar energy, we reduce reliance on finite fossil fuels, thereby cutting down greenhouse gas emissions and combating climate change. Additionally, solar power systems can significantly lower electricity bills over time, offering financial savings and enhancing energy independence for homes and businesses alike.
However, there are notable drawbacks to consider. The initial cost of installing solar panels and associated equipment can be substantial, although this is offset by long-term savings on energy bills. Furthermore, solar power generation is inherently dependent on sunlight availability, making it less effective in regions with frequent cloud cover or heavy shading. To mitigate this limitation, supplementary energy storage solutions like batteries may be required, adding to the overall investment.
Despite these challenges, ongoing technological advancements and decreasing costs are making solar power increasingly accessible and efficient. Innovations in panel design, improved efficiency of solar cells, and better storage solutions are continually enhancing the viability and attractiveness of solar energy as a sustainable choice for powering homes, businesses, and communities across India and beyond.
Applications of Solar Energy
Solar energy is incredibly versatile, finding applications across diverse sectors. In residential settings, solar panels offer a sustainable solution to meet electricity needs, reducing dependency on conventional grid power and effectively lowering energy bills over time. This makes solar power particularly appealing for homeowners seeking to embrace renewable energy solutions while minimizing their environmental footprint.
In the commercial and industrial sectors, solar energy plays a pivotal role in powering large-scale operations such as factories, warehouses, and office buildings. By integrating solar power into their infrastructure, businesses can not only reduce operational costs but also demonstrate a commitment to sustainable practices, aligning with global environmental goals.
Moreover, solar energy extends its reach to remote or off-grid areas where establishing traditional power infrastructure is challenging or costly. Here, solar installations provide reliable electricity access, enhancing quality of life and supporting community development initiatives.
In transportation, solar energy contributes to the growing trend of sustainable mobility through solar-powered vehicles and charging stations. This application not only reduces reliance on fossil fuels but also promotes cleaner air and reduced carbon emissions.
Overall, the adaptability and sustainability of solar energy make it a valuable asset across various fields, driving environmental stewardship, energy efficiency, and economic savings throughout India and beyond.
Conclusion
The future of solar power in renewable energy is promising. As technology continues to advance, the efficiency and affordability of solar power systems are expected to improve. Innovations in solar cell materials and energy storage solutions will enhance the viability of solar energy, making it a more integral part of the global energy mix. Governments and organizations worldwide are investing in solar power, recognizing its potential to reduce carbon footprints and provide sustainable energy solutions. With ongoing research and development, solar power is poised to play a crucial role in achieving a clean and renewable energy future.
