How to calculate safety distance?
Key Takeaway
To calculate the safety distance for machinery with a safety light curtain or similar protective equipment, you use the hand speed constant (K) and the stopping time of the machine. The standard hand speed used is 63 inches per second, according to ANSI B11.19-1990. The formula to calculate the safety distance ( S ) is:
[ S = K times T ]
Where:
– ( S ) is the minimum safety distance in inches,
– ( K ) is the hand speed constant (63 inches/second is commonly used),
– ( T ) is the stopping time of the machine from the moment the safety device is triggered to when the machine actually stops, measured in seconds.
This calculation ensures that the safety distance is sufficient to prevent access to hazardous areas before the machine can stop, providing crucial protection for operators.
What is Safety Distance?
Safety distance plays a crucial role in workplace safety, especially around heavy machinery and automated systems. It is the calculated space required to keep workers safe from harm when they interact with or are in proximity to machines. This distance ensures that by the time a person can reach into a dangerous zone, safety measures have already activated to halt machine operation. Thus, it is a preventive measure, designed to give enough time for a machine to stop and for a person to avoid contact with moving parts.
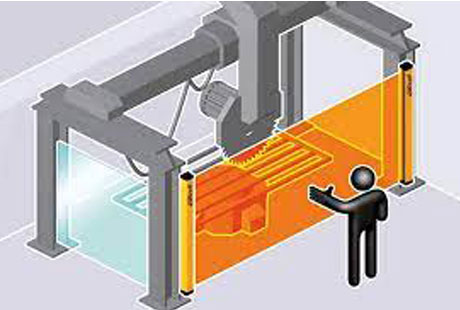
Required Data for Calculating Safety Distance
Calculating safety distance accurately requires several critical pieces of data: the speed at which an individual can approach the machine, the response time of the safety mechanism (such as emergency stops or light curtains), and the machine’s stopping time from the moment a risk is detected. Environmental factors, such as the layout of the workspace and operational pace, must also be considered. These elements help define the minimum safe distance necessary to prevent accidents effectively.
Factors Influencing Safety Distance
The safety distance is influenced by multiple factors including machine type, operation speed, and the environment. Factors such as flooring conditions, lighting, and the presence of any obstacles that could affect a person’s ability to move quickly or safely are also crucial. Psychological factors, like a worker’s preparedness and reaction time, can significantly impact the required safety distance. Each of these factors must be evaluated and adjusted accordingly to ensure the safety measures are effective under all operating conditions.
Detailed Calculation Process
The formula for calculating safety distance typically incorporates the hand speed of the approach (speed at which a person can reach towards the hazard), the response time of the safety mechanism, and the stopping time of the machine. This can be expressed as: Safety Distance = (Hand Speed × Response Time) + Machine Stopping Distance. This calculation ensures that even in a worst-case scenario, the machinery has sufficient time to cease operation before a person can come into contact with any dangerous component.
Adjusting Safety Distance for Different Machines
Because each machine operates differently with varying risks and stopping times, safety distance calculations must be customized. A machine with a longer stopping time requires a greater safety distance, while a faster-responding machine might need less. Regular reassessment of these distances is crucial, particularly if there are changes to the machine’s operational parameters or to the environment that could influence the effectiveness of existing safety measures.
Conclusion
Effective safety distance calculations are vital for protecting workers in environments with mechanical hazards. By meticulously determining and implementing these distances, workplaces can significantly mitigate the risk of injuries, ensuring a safer environment for all employees. Continuous monitoring and adjustment of safety protocols, based on operational and environmental changes, are essential for maintaining these safety standards.
