How To Connect Ir Sensor To Relay?
Key Takeaway
To connect an IR sensor to a relay, follow these straightforward steps, ensuring that all connections are secure and correctly configured:
Connect the output pin of the IR sensor to the input signal pin on the relay module. This setup is crucial as it allows the IR sensor’s signal to trigger the relay.
Attach the Vcc (positive power supply) of the relay module to the Vcc rail on your breadboard or equivalent power source.
Link the ground pin of the relay module to the ground rail of the breadboard. This common ground prevents potential issues with different voltage levels that could disrupt the circuit.
If using a microcontroller like an Arduino, connect the control pin of the relay to a digital output on the Arduino to manage the relay operations programmatically.
This connection allows the IR sensor to activate the relay when it detects the specified infrared signal, enabling control over devices connected to the relay.
Fundamentals of IR Sensors and Relays
IR (Infrared) sensors and relays are essential components in modern automation systems. IR sensors detect infrared radiation, which is invisible to the human eye but can be emitted by all objects above absolute zero. They are used in various applications, from motion detection to distance measurement. Relays, on the other hand, are electrically operated switches that allow a low-power signal to control a higher power circuit. By integrating IR sensors with relays, engineers can create automated systems that respond to physical changes detected by the IR sensors, enabling a wide range of functionalities.
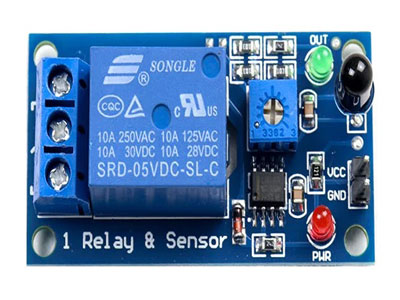
Detailed Instructions for Wiring IR Sensors to Relays
Connecting an IR sensor to a relay involves several straightforward steps to ensure seamless integration and functionality. Here’s how you can do it:
1. Identify Terminals: Begin by locating the output terminals on the IR sensor and the input terminals on the relay coil. Understanding the correct terminals is crucial for proper wiring and operation.
2. Power Connections: Connect the power supply to both the IR sensor and the relay. Make sure the voltage levels are compatible with the requirements of both components to avoid damage or malfunction.
3. Sensor to Relay Connection: Link the output of the IR sensor to the input of the relay coil. This connection is vital as it allows the IR sensor to send a signal to the relay when it detects infrared radiation, triggering the relay.
4. Load Connection: Connect the common (COM) terminal of the relay to the power source. Then, connect the normally open (NO) terminal to the device you want to control. This setup ensures that the device is powered only when the relay is activated by the sensor.
5. Testing: Finally, power up the system and test the IR sensor by exposing it to infrared light. Observe whether the relay activates and powers the connected device. If the relay responds correctly, your setup is successful.
By following these steps meticulously, you can ensure a reliable and efficient connection between an IR sensor and a relay, enhancing automation in your applications.
Applications and Benefits of IR Sensor-Relay Configurations
IR sensor-relay configurations are employed in a wide range of applications due to their efficiency and reliability. Here are some key uses and advantages:
Security Systems: In security systems, IR sensors detect motion and trigger relays to sound alarms or activate lights. This immediate response helps in deterring intruders and ensuring the security of premises. The ability to automate security measures without human intervention enhances safety and reduces the need for constant monitoring.
Automatic Lighting: IR sensors control lighting in residential and commercial buildings, turning lights on when motion is detected and off when the area is unoccupied. This application is particularly beneficial in reducing energy wastage and ensuring lights are only used when necessary. It enhances convenience and promotes energy efficiency, contributing to lower utility bills.
Industrial Automation: In manufacturing, IR sensors monitor production lines and control machinery via relays, enhancing efficiency and safety. By automating the operation of machinery based on real-time data from IR sensors, production processes become more streamlined, and the risk of human error is minimized. This leads to higher productivity and improved safety standards.
Energy Management: By controlling HVAC systems based on occupancy, IR sensors and relays help reduce energy consumption. These systems ensure that heating, ventilation, and air conditioning are only active when needed, leading to significant energy savings. In large buildings and offices, this can translate into substantial cost reductions and a lower environmental impact.
Overall, the integration of IR sensors with relays provides numerous benefits across various sectors, making operations more automated, efficient, and sustainable. This combination is a cornerstone of modern automation systems, offering both functional and economic advantages.
Troubleshooting Tips for IR Sensor-Relay Setups
IR sensor-relay setups can encounter several issues, but these can often be resolved with some straightforward troubleshooting tips:
No Response: If the setup does not respond at all, first ensure all connections are secure and the power supply is stable. Check that both the IR sensor and the relay are receiving the correct voltage as specified by their datasheets. Faulty power supplies or loose connections are common causes of non-responsiveness.
False Triggering: Electrical noise can cause the relay to trigger falsely. This can be mitigated by using shielded cables and ensuring proper grounding of the system. Additionally, placing the IR sensor away from sources of electrical noise, such as motors or other high-power devices, can reduce false triggers.
Sensor Range Issues: If the IR sensor’s range is inadequate, check for any obstructions that might block the infrared beam. Ensure the sensor is positioned correctly and aimed at the intended detection area. Sometimes, adjusting the sensitivity settings of the sensor or choosing a sensor with a more suitable range can solve the issue.
Relay Not Activating: If the relay does not activate when the sensor detects a signal, verify that the sensor’s output signal is sufficient to trigger the relay. In some cases, the output signal from the sensor may be too weak to activate the relay. Using a signal amplifier or choosing a relay with a lower activation threshold can help resolve this problem.
By systematically addressing these common issues, you can ensure that your IR sensor-relay setup operates reliably and effectively. Regular maintenance and checks can also preempt potential problems, maintaining optimal performance in your automated systems.
Innovative Uses of IR Sensors and Relays in Automation
Innovative applications of IR sensors and relays are continuously emerging in various fields, showcasing their versatility and enhancing automation systems:
Smart Homes: In modern smart homes, IR sensors and relays are pivotal in automating home appliances. They control lighting, HVAC systems, and security devices, contributing to energy-efficient and convenient living environments. For example, IR sensors can detect when a person enters a room, triggering the relay to turn on the lights or adjust the temperature.
Healthcare: In healthcare settings, IR sensors play a crucial role in monitoring patient movement and controlling medical equipment. They enhance patient care and safety by automatically adjusting beds, monitoring vital signs, or controlling lighting based on patient activity. This automation allows healthcare providers to focus more on patient care while ensuring a safe and comfortable environment.
Retail: Retail stores leverage IR sensors and relays to track customer movement and control lighting and displays. These sensors can detect the presence of customers, activating relays to adjust lighting, play promotional videos, or highlight specific products. This dynamic control not only enhances the shopping experience but also improves energy efficiency by reducing unnecessary power consumption.
Agriculture: In agriculture, IR sensors monitor crop conditions such as moisture levels and temperature. Relays control irrigation systems based on real-time data from these sensors, optimizing water usage and improving crop yield. This automation reduces water waste, enhances crop health, and increases agricultural productivity, making farming more sustainable.
By integrating IR sensors and relays, various industries can achieve higher levels of automation, efficiency, and productivity. These innovative uses not only streamline operations but also provide significant benefits in terms of energy savings, safety, and overall system performance.
Conclusion
Integrating IR sensors with relays is a powerful method to streamline operations in various domains. By following proper installation procedures and understanding the fundamentals, engineers can create reliable and efficient automated systems. These integrations offer significant benefits, from enhancing security and reducing energy consumption to improving industrial and agricultural processes. With ongoing innovations, the applications of IR sensor-relay configurations will continue to expand, driving advancements in automation and control technologies.
