How To Connect Sensor To Relay?
Key Takeaway
To connect a sensor to a relay, first ensure that the relay’s operating voltage and current specifications are compatible with the sensor. Most NPO sensors, for example, can handle a maximum of 20mA. Choose a relay with a coil or input resistance that draws less than 20mA at the sensor’s Vcc (supply voltage). Here’s how to connect them:
Connect the sensor’s output to the relay’s input.
Ensure the sensor’s ground is connected to the relay’s ground.
Apply the sensor’s Vcc to the relay.
Test the connection by activating the sensor to see if the relay switches correctly.
This setup ensures that the relay operates safely without exceeding the current limit of the sensor, preventing potential damage.
Basics of Integrating Sensors with Relays
Integrating sensors with relays forms the backbone of many automation systems. Sensors detect changes in the environment, such as temperature, light, or motion, and send signals to relays, which then control other devices like lights, alarms, or motors. Understanding the basics of how sensors and relays work together is crucial for creating efficient and responsive systems. Sensors typically produce low-power signals, which are insufficient to directly operate high-power devices. Relays, acting as intermediaries, use these low-power signals to switch high-power circuits on or off, ensuring that the system operates safely and effectively.
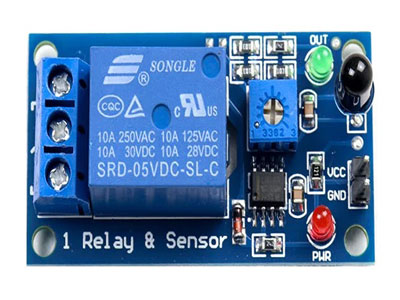
Step-by-Step Connection Guide for Sensor and Relay Systems
Connecting a sensor to a relay involves a few straightforward steps, but precision is key to ensure reliability and functionality. Start by identifying the output terminals of the sensor and the input terminals of the relay coil. This is crucial as mismatched connections can lead to malfunction. Next, connect the sensor’s output to the relay’s input, ensuring the voltage levels are compatible. This step often involves matching the sensor’s signal voltage to the relay’s operating voltage.
After establishing the sensor-to-relay connection, connect the common terminal (COM) of the relay to the power source. The normally open (NO) terminal of the relay should be connected to the device you intend to control, such as a motor or light. When the sensor detects the specific condition it is designed to monitor, it sends a signal to the relay. This signal energizes the relay coil, causing the relay to switch from its default position (COM to NC) to the NO position, thereby activating the connected device.
Ensure all connections are secure and follow the wiring diagram closely to prevent errors. Double-check each connection for proper insulation and tightness to avoid short circuits or loose connections, which can affect performance. By carefully following these steps, you can create a reliable sensor-relay setup that enhances your system’s automation capabilities.
Tips for Selecting Compatible Sensors and Relays
Selecting the right sensors and relays is essential for ensuring reliable operation in your automation systems. Start by identifying the type of sensor that suits your application—whether it’s for temperature, motion, light, or another parameter. Ensure the sensor’s output signal is compatible with the relay’s input requirements, typically checking voltage and current ratings to avoid mismatch issues.
It’s crucial to verify that both the sensor and relay can handle the expected load. For instance, if the sensor outputs a low voltage signal, ensure the relay can be triggered by this voltage level. In such cases, choosing a low voltage relay would be appropriate. Additionally, consider the environmental conditions where the components will be used. Factors such as temperature, humidity, and electromagnetic interference can impact sensor performance and relay operation.
Opt for components from reputable manufacturers to guarantee quality and reliability. Consulting datasheets is also vital; they provide detailed information on electrical characteristics, operational limits, and environmental tolerances, helping you make informed decisions. By carefully selecting compatible sensors and relays, you can create a robust and efficient control system tailored to your specific needs. This approach minimizes the risk of operational failures and enhances the overall effectiveness of your automation setup.
Common Challenges and Solutions in Sensor-Relay Integration
Integrating sensors with relays can present several challenges. One common issue is signal incompatibility, where the sensor’s output is not sufficient to trigger the relay. This problem can be resolved by using signal conditioning circuits, such as amplifiers or optocouplers, which boost the sensor’s signal to a level that can activate the relay effectively.
Another challenge is dealing with electrical noise, which can cause false triggering of the relay. Electrical noise can come from various sources, including nearby electrical equipment and power lines. To mitigate this problem, use shielded cables and proper grounding techniques. Shielded cables help protect the signal from external interference, while proper grounding reduces the risk of noise affecting the system’s performance.
Additionally, ensuring that the power supply is stable and within the specified range for both the sensor and the relay is crucial for reliable operation. Fluctuations in power supply can cause inconsistent performance or even damage the components. Using a regulated power supply can help maintain a consistent voltage level, ensuring both the sensor and relay operate reliably.
By addressing these common challenges with appropriate solutions, you can achieve a robust and reliable integration of sensors and relays, enhancing the overall performance and reliability of your automation system. This approach minimizes the risk of operational disruptions and ensures smooth, efficient control of your systems.
Best Practices for Ensuring Reliable Sensor-Relay Operations
To ensure reliable operation of sensor-relay systems, adhere to several best practices. Start by regularly inspecting all connections for wear or corrosion, ensuring they remain secure and effective. This helps prevent unexpected failures and maintains optimal performance. Use proper enclosures to protect components from environmental factors such as dust, moisture, and extreme temperatures, which can significantly impact the reliability and lifespan of the system.
Implement routine testing and maintenance schedules to identify and rectify issues early. Regular testing ensures that the system is functioning correctly and helps in detecting potential problems before they cause significant disruptions. Additionally, consider incorporating redundancy in critical systems to maintain functionality in case of component failure. This means having backup components or parallel systems that can take over if one part fails, ensuring continuous operation.
Properly label all wiring and document the system configuration. Clear labeling and thorough documentation facilitate easier troubleshooting and future upgrades. When issues arise, or when it’s time to expand or modify the system, well-documented configurations can save time and reduce errors.
By following these best practices, you can enhance the reliability and longevity of your sensor-relay systems, ensuring they operate smoothly and efficiently. This approach not only minimizes downtime but also ensures that your systems are robust and adaptable to future needs.
Conclusion
Connecting sensors to relays is a fundamental aspect of modern automation systems, enhancing efficiency and responsiveness. By understanding the basics, following a structured connection guide, selecting compatible components, addressing common challenges, and adhering to best practices, engineers can create robust and reliable sensor-relay systems. These connections play a vital role in various applications, from industrial automation to home security, ensuring that systems operate smoothly and effectively. Investing time in proper setup and maintenance can significantly enhance the performance and longevity of these automated systems, providing valuable benefits in terms of safety, efficiency, and convenience.
