What Are The Key Components In A Machine Vision System?
Key Takeaway
A machine vision system consists of several key components. The primary components include lighting, which illuminates the object for clear image capture, and the lens, which focuses the image onto the image sensor. The image sensor then converts the visual information into a digital format.
Vision processing is another critical component, where the captured images are analyzed using specialized software to extract useful information. Finally, communications enable the system to interface with other machines or control systems, allowing for automated decision-making and action based on the processed data. These components work together to provide accurate and efficient visual inspection and analysis in various industrial applications.
Image Acquisition
Welcome to the dynamic world of machine vision systems! As a fresh engineer stepping into this innovative field, it’s crucial to understand the core components that make these systems so effective. Each element works synergistically to transform visual data into actionable insights, propelling industries towards greater automation and precision.
The first step in any machine vision system is image acquisition. This is where cameras and sensors come into play, capturing raw visual data from the environment. The quality of image acquisition directly impacts the system’s performance, making it essential to choose the right camera—be it high-resolution, infrared, or high-speed—based on the application’s specific needs. This component is the system’s eyes, laying the foundational data that will flow through the rest of the process.
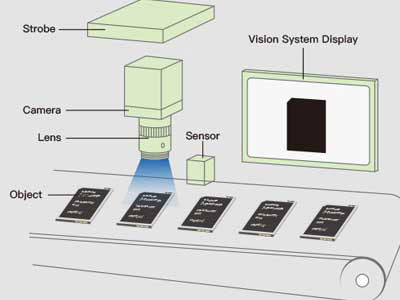
Image Processing
Picture this: A system that can not only see but also understand what it sees—transforming raw images into actionable insights. Image processing is akin to our brain interpreting what our eyes see, converting raw image data into useful information. It involves several key tasks such as noise reduction, contrast enhancement, edge detection, and object recognition.
Algorithms are crucial in this process. They analyze images, identify patterns, and extract relevant information. For instance, in a packaging line, image processing ensures that labels are correctly placed and readable. Advanced systems use machine learning algorithms to enhance their accuracy, adapting to new types of defects over time.
In the industrial sector, efficient image processing is essential. It enhances productivity and reduces errors. As a newly joined engineer, grasping the fundamentals of image processing is invaluable. This technology bridges the gap between raw data and actionable insights, making systems smarter and more reliable.
By mastering image processing, you’re not just learning a technology—you’re equipping yourself with the tools to drive innovation and efficiency in any industrial setting. Understanding and applying these principles will make you a valuable asset in the industry.
Optics and Illumination
Imagine trying to read a book in the dark. The right lighting can make all the difference in seeing the details clearly. Similarly, machine vision systems rely heavily on optics and illumination. Just as the quality of our vision depends on lighting and lenses, these systems need the right combination of lenses and lighting to capture clear and accurate images.
Proper lighting is essential. It highlights important features for inspection while minimizing shadows and glare. Different lighting techniques, such as backlighting, front lighting, and structured lighting, are chosen based on the specific application. For instance, backlighting can make edges more visible, while structured lighting can enhance surface details.
Optics, including lenses and filters, play a crucial role in refining the image. They focus and enhance details necessary for precise analysis. A well-chosen lens ensures that the system captures the necessary information with high accuracy. Filters can be used to eliminate unwanted light and improve image clarity.
As a new engineer, understanding the importance of optics and illumination is key. These components ensure that machine vision systems perform reliably under various conditions, making them indispensable in industrial applications. Mastering this knowledge will enable you to optimize system performance and drive quality improvements in your processes.
Software and Algorithms
Think of this as the control center of the system, where all the data is processed and decisions are made. Behind every efficient machine vision system lies powerful software and sophisticated algorithms. The software integrates all components and executes the image processing tasks, acting as the brain of the system. Algorithms, meanwhile, are the instructions that guide the system on how to analyze images and extract meaningful information.
The software handles everything from initial image capture to final analysis, providing a user-friendly interface for configuration and monitoring. It ensures seamless operation and allows users to customize settings to suit specific needs. Algorithms can range from simple thresholding techniques to complex machine learning models. In industries like semiconductor manufacturing, these algorithms are crucial for identifying minute defects that are invisible to the naked eye.
As a new engineer, understanding the role of software and algorithms in machine vision systems is essential. These components ensure precise analysis and reliable performance. By mastering these elements, you can optimize machine vision systems to enhance quality control and drive innovation in your field. This knowledge equips you to tackle complex challenges and improve operational efficiency in industrial applications.
Communication Interfaces
Finally, for a machine vision system to be truly effective, it must communicate with other devices and systems. Communication interfaces enable this interaction, ensuring that the data collected and analyzed by the vision system can be used for making real-time decisions. These interfaces can be wired or wireless, depending on the industrial setup.
Hook: Imagine a well-orchestrated symphony where every instrument needs to play in harmony—communication interfaces ensure seamless integration.
In a production environment, the vision system often needs to send data to a central control unit or other machinery. For instance, if a defect is detected, the system can alert the production line to halt, ensuring defective products do not reach the customer. Standard communication protocols like Ethernet, USB, and fieldbus systems are commonly used.
Conclusion
In summary, understanding the key components of a machine vision system is vital for any engineer stepping into this field. Each component—from image acquisition to communication interfaces—plays a critical role in ensuring the system’s accuracy and efficiency. By mastering these elements, you can contribute to the development of more reliable and advanced automation solutions, driving innovation in the industry.
Hook: With this knowledge, you’re now equipped to delve deeper into the world of machine vision, ready to tackle challenges and optimize processes in your field.
By combining high-quality cameras, robust image processing algorithms, precise optics and illumination, powerful software, and reliable communication interfaces, machine vision systems become indispensable tools in modern manufacturing and quality control. Your journey in this domain promises to be both exciting and impactful, as you help push the boundaries of what automation can achieve.
