What Is A Serial Signal?
Key Takeaway
A serial signal is a type of communication method where data is transmitted one bit at a time over a single transmission line. This method is used in serial communication, allowing devices to send and receive data using just one or two lines, making it simple and efficient.
In serial communication, the data bits are sent sequentially, often using standards like RS-232, RS-422, or RS-485. This is different from parallel communication, where multiple bits are sent simultaneously over multiple lines. Serial signals are widely used in various applications, including computer peripherals, industrial automation, and telecommunications, due to their simplicity and long-distance communication capabilities.
Basics of Serial Communication Signals
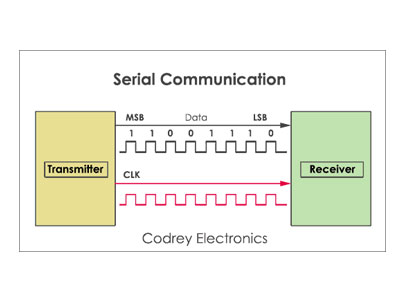
Serial communication involves the sequential transmission of bits over a single communication channel. Unlike parallel communication, where multiple bits are sent simultaneously, serial communication sends bits one after another, which reduces the complexity of wiring and improves reliability over long distances. Key elements of serial communication include:
Start and Stop Bits: These bits signal the beginning and end of a data packet, ensuring that the receiver can accurately frame the data.
Baud Rate: The speed of data transmission, measured in bits per second (bps). Common baud rates include 9600, 19200, and 115200 bps.
Parity Bit: An optional bit used for error checking, which helps detect errors in the transmitted data.
Types of Serial Signals in Networking
There are several types of serial signals used in networking, each with its specific characteristics and applications:
RS-232: One of the oldest and most common serial communication standards, typically used for short-distance communication between computers and peripheral devices.
RS-485: Supports longer distances and multiple devices on the same bus, making it ideal for industrial environments where robust communication is required.
USB: A modern standard that supports high-speed data transfer and provides power to connected devices, commonly used in personal computers and consumer electronics.
Ethernet: Although not a traditional serial signal, Ethernet serial devices convert serial signals to Ethernet frames, enabling network communication over longer distances and higher speeds.
Each type of serial signal addresses specific networking challenges, providing solutions for various communication needs.
You May Like to Read
How Serial Signals Are Used in Data Transmission
Serial signals are crucial for data transmission, enabling communication between various devices. The process starts by converting data into a serial format, transmitting it bit by bit over a single communication channel, and then converting it back into parallel data at the receiver’s end. This method is efficient for long-distance communication and minimizes the number of physical connections required, reducing complexity and cost.
In industrial settings, serial signals play a vital role in transmitting sensor data from remote locations to a central control system. This real-time data flow is essential for monitoring and controlling industrial processes. For instance, temperature sensors in a factory might send continuous data to a central control room, where operators can make adjustments to maintain optimal conditions.
Similarly, in telecommunications, serial signals enable seamless communication between network devices over extensive distances. They ensure reliable and continuous data flow, critical for maintaining network stability and performance. The use of start and stop bits, along with correctly configured baud rates and parity bits, helps maintain data integrity and accuracy during transmission, reducing errors and ensuring smooth operation.
By understanding and utilizing serial signals effectively, industries can achieve robust and reliable data communication, essential for modern networking and industrial automation.
Advantages of Serial Signals in Industrial Networks
Serial signals offer several advantages in industrial networks:
Long-Distance Communication: Serial signals can transmit data over long distances with minimal signal degradation, making them ideal for large industrial sites.
Reduced Complexity: Serial communication requires fewer wires compared to parallel communication, reducing the complexity and cost of installation.
Robustness: Standards like RS-485 provide high noise immunity and the ability to connect multiple devices on the same bus, enhancing reliability in harsh industrial environments.
Versatility: Serial signals can interface with various devices and systems, providing flexibility in integrating new technology with existing infrastructure.
These advantages make serial signals a preferred choice for ensuring efficient and reliable data communication in industrial networks.
Troubleshooting Serial Signal Issues
Troubleshooting serial signal issues involves several steps to identify and resolve communication problems:
Check Connections: Ensure that all cables and connectors are securely attached and in good condition. Loose or damaged connections can cause data transmission errors.
Verify Settings: Confirm that the baud rate, parity, data bits, and stop bits are correctly configured on both the transmitting and receiving devices. Mismatched settings can lead to communication failures.
Test Cables: Use a cable tester to check for faults in the communication cable. Faulty cables can degrade signal quality and cause intermittent issues.
Monitor Signal Quality: Use an oscilloscope or signal analyzer to monitor the quality of the serial signal. Look for signal degradation, noise, or other anomalies that could affect data transmission.
Update Firmware: Ensure that the firmware on all devices is up to date. Firmware updates can resolve known issues and improve communication reliability.
By systematically addressing these potential issues, you can ensure efficient and reliable data transfer using serial signals.
Conclusion
Serial signals play a crucial role in ensuring efficient data transfer across various communication networks. Understanding the basics of serial communication, different types of serial signals, and their applications helps in leveraging their advantages in industrial and networking environments. By implementing best practices for troubleshooting and optimizing serial signal use, you can enhance the reliability and efficiency of your communication systems, ensuring seamless and effective data transmission in diverse applications.
