What Is A Synchronous Motor?
Key Takeaway
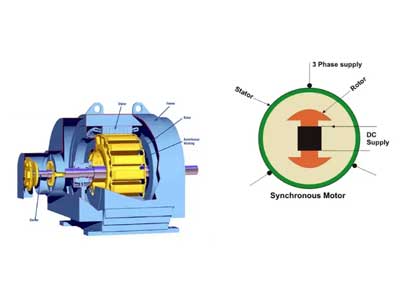
A synchronous motor is an AC motor that operates at a constant speed, synchronized with the frequency of the supply current. Unlike an induction motor, it requires an external source of DC power for the rotor to create a constant magnetic field. The rotor’s speed matches the rotating magnetic field in the stator, ensuring precise speed control. Synchronous motors are commonly used in applications where constant speed is crucial, such as clocks, record players, and synchronous clocks. Understanding synchronous motors is essential for applications requiring precise speed and timing.
Definition and Working Principle of Synchronous Motors
A synchronous motor is an AC motor that operates at a constant speed, regardless of the load, once it reaches synchronous speed. The rotor of the motor rotates in sync with the magnetic field generated by the stator. This synchronization is achieved by applying a direct current (DC) to the rotor windings, creating a magnetic field that locks in step with the rotating magnetic field of the stator. This mechanism ensures that the motor maintains a constant speed, making it ideal for applications requiring precise speed control.
Types of Synchronous Motors
Synchronous motors come in two primary types: non-excited and direct current (DC) excited. Non-excited synchronous motors rely on permanent magnets or reluctance to achieve synchronization with the stator’s rotating magnetic field. These motors are simpler in design, maintenance-free, and are typically used in applications where ease of use and reliability are paramount. Their straightforward construction makes them cost-effective and ideal for less demanding industrial applications.
DC excited synchronous motors, however, use an external DC power source to supply current to the rotor windings. This excitation creates a strong magnetic field that can be precisely controlled, providing better performance in terms of torque and efficiency. These motors are more versatile and suitable for heavy-duty industrial applications where precise control and high performance are required. Within this category, there are two further classifications: salient pole and non-salient pole motors.
Salient pole motors feature protruding poles on the rotor, making them suitable for applications requiring low to medium speeds, such as hydroelectric generators. Non-salient pole motors, with a cylindrical rotor, are used in high-speed applications like turbo generators due to their smooth and balanced operation.
Understanding the types and specific characteristics of synchronous motors helps in selecting the right motor for a given application, ensuring optimal performance and longevity.
Applications of Synchronous Motors
Synchronous motors are essential in industrial applications requiring precise speed and position control. Their capability to maintain a constant speed regardless of load variations makes them invaluable in various sectors. In power generation, large synchronous motors drive generators, ensuring stable and efficient electricity production. In manufacturing, they power conveyor systems, milling machines, and other critical equipment, providing consistent and reliable operation.
In the textile industry, synchronous motors drive machinery in mills, ensuring uniformity in production processes. Similarly, in paper mills, their constant speed operation ensures high-quality output. Chemical processing plants utilize these motors to maintain precise control over processing speeds, enhancing efficiency and product consistency.
Additionally, synchronous motors are integral to HVAC systems and pumps, where efficiency and reliability are paramount. In HVAC systems, they help maintain optimal climate conditions by driving fans and compressors. In pumping applications, they ensure consistent fluid flow, crucial for processes in water treatment plants and other industrial setups.
The versatility and reliability of synchronous motors make them indispensable across various industries, highlighting their role in enhancing operational efficiency and productivity. Understanding their applications helps engineers and technicians choose the right motor for their specific needs, ensuring optimal performance and longevity.
Advantages and Disadvantages of Synchronous Motors
Synchronous motors offer numerous advantages that make them highly valuable in various industrial applications. One of their primary benefits is high efficiency, which ensures minimal energy loss during operation. This efficiency translates into lower operational costs and reduced energy consumption, making them ideal for industries focused on sustainability. Additionally, synchronous motors provide precise speed control, maintaining constant speed regardless of load variations. This feature is crucial for applications requiring exact speed and position control, such as manufacturing and processing industries.
Another significant advantage is their ability to improve power factor correction. By operating at a leading power factor, synchronous motors can compensate for lagging power factors in other equipment, enhancing overall system efficiency and reducing energy costs. This capability makes them beneficial in scenarios where power quality is a concern.
However, synchronous motors also have some disadvantages. They have complex starting mechanisms, often requiring auxiliary devices to bring them up to synchronous speed before they can operate efficiently. This complexity can increase initial setup costs and maintenance requirements. Moreover, these motors require a separate DC power source for excitation, adding to the system’s overall complexity and potential points of failure.
Synchronous motors can also be more expensive than other types of motors, both in terms of initial cost and maintenance. Regular maintenance is necessary to ensure optimal performance, which can increase operational costs over time. Despite these drawbacks, the advantages of synchronous motors in terms of efficiency, speed control, and power factor correction often outweigh the disadvantages, especially in applications where precision and reliability are critical.
Maintenance and Troubleshooting of Synchronous Motors
Regular maintenance is vital for the reliable operation of synchronous motors. Essential maintenance tasks include inspecting and cleaning the motor windings, which helps prevent dust and debris from causing insulation breakdown or overheating. Checking the condition of the bearings is also crucial, as worn or damaged bearings can lead to rotor misalignment and excessive vibration. Ensuring proper lubrication of the bearings can prevent friction and wear, extending the motor’s lifespan.
Troubleshooting common issues involves using diagnostic tools like multimeters and insulation resistance testers. For instance, a multimeter can help identify electrical faults such as open or short circuits in the windings. Insulation resistance testers are used to detect insulation breakdown, which can lead to electrical leaks and potential motor failure. Addressing these issues promptly can prevent more significant problems and minimize downtime.
Rotor misalignment is another common issue that can affect motor performance. Misalignment can cause uneven wear on bearings and increased vibration, leading to potential mechanical failure. Regularly checking and realigning the rotor can mitigate this risk. Additionally, monitoring the motor’s temperature and vibration levels can provide early warning signs of potential issues, allowing for proactive maintenance.
Implementing a regular maintenance schedule and promptly addressing any identified issues can significantly enhance the reliability and efficiency of synchronous motors. This proactive approach ensures that the motors operate smoothly, reduces the risk of unexpected failures, and extends the overall lifespan of the equipment.
Conclusion
Synchronous motors play a critical role in various industrial applications due to their ability to provide precise speed control and high efficiency. They are indispensable in sectors where constant speed and reliability are paramount, such as manufacturing, power generation, and HVAC systems. Understanding the working principles, types, advantages, and maintenance requirements of synchronous motors is crucial for engineers and technicians to optimize their performance and ensure the smooth operation of industrial processes. By leveraging the benefits of synchronous motors, industries can achieve greater efficiency, reduce energy costs, and improve overall productivity.
