What Is The Difference Between Muting And Blanking Light Curtains?
Key Takeaway
Muting and blanking are distinct functions of safety light curtains, each serving different purposes in industrial safety management. Muting refers to the temporary suspension of the light curtain’s safety functions, allowing objects such as materials being processed to pass through the detection zone without triggering a machine stop. This function is particularly useful during normal production cycles where no human risk is present. Blanking, on the other hand, involves permanently disabling one or more beams of the light curtain to accommodate stationary objects like fixtures or parts of the machinery within the detection zone. Unlike muting, which is activated only during specific conditions, blanking is a constant state that allows the light curtain to ignore selected obstructions while continuing to monitor for unexpected interruptions. The primary difference between the two is that muting is a conditional and temporary adjustment to the light curtain’s function, while blanking is a permanent alteration to its detection pattern.
Basics of Light Curtain Functions
Light curtains are safety devices that create an invisible barrier using infrared light beams. These beams form a protective screen around dangerous machinery, detecting any interruptions and triggering safety responses, such as stopping the machine. Light curtains enhance safety without impeding workflow, making them essential in automated and high-risk environments. They come with advanced features like muting and blanking to offer greater flexibility and efficiency.
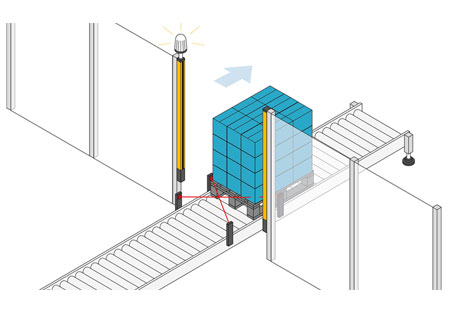
What is Muting? Definition and Applications
Muting is a feature that temporarily deactivates the safety function of light curtains, allowing specific, pre-determined objects to pass through without stopping the machine. This is particularly useful in automated processes where materials need to move through protected areas, such as on a conveyor belt. Muting sensors detect the presence of these authorized objects and activate the muting function, enabling continuous operation. Once the object has passed, the light curtain resumes its normal protective function. Muting is ideal for applications where maintaining a steady workflow is crucial, such as packaging, material handling, and assembly lines.
You May Like to Read
What is Blanking? Definition and Applications
Blanking is a feature that selectively deactivates certain beams within the light curtain, allowing objects of specific shapes and sizes to pass through the safety zone without triggering a stop. This function is useful when parts of a machine or materials must regularly move through the protective field. Blanking can be static or dynamic. Static blanking deactivates fixed beams, while dynamic blanking adjusts to moving parts, providing flexibility for various operations. Blanking is particularly beneficial in processes involving irregularly shaped objects or complex machinery, such as robotic arms or automated welders.
Operational Differences Between Muting and Blanking
While both muting and blanking enhance the functionality of light curtains, they operate differently. Muting temporarily disables the entire safety function for specific objects, allowing them to pass without stopping the machine. In contrast, blanking deactivates only certain beams, permitting parts of an object to move through the safety zone. Muting is typically used for materials or products that need to pass through frequently and predictably, whereas blanking is suited for more complex, variable scenarios where parts of machinery need to interact with the safety field. Understanding these operational differences helps in selecting the appropriate feature based on the specific requirements of your application.
Choosing Between Muting and Blanking for Specific Applications
Selecting between muting and blanking depends on your specific operational needs. If your process involves regular, predictable movement of materials through a safety zone, muting is likely the best choice. It ensures uninterrupted workflow without compromising safety. On the other hand, if your operations involve complex machinery or irregularly shaped objects that need to move through the safety field, blanking offers the flexibility required to maintain both safety and efficiency. Evaluating the nature of your operations, the types of objects involved, and the frequency of their movement through safety zones will guide you in choosing the right light curtain feature.
Conclusion
In conclusion, understanding the difference between muting and blanking is crucial for configuring light curtains effectively in industrial environments. Both features enhance safety and efficiency, but their applications vary based on operational requirements. Muting is ideal for consistent, predictable processes, while blanking provides flexibility for complex, variable scenarios. By carefully assessing your specific needs and understanding how each feature operates, you can ensure that your light curtains provide optimal protection and productivity. Implementing best practices in light curtain configuration not only safeguards workers but also enhances overall operational efficiency, making these devices indispensable in modern industrial settings.
