Why Do We Use Photoelectric Sensors?
Key Takeaway
Photoelectric sensors are vital in modern automation for their precision and rapid response times. They operate without physical contact, minimizing wear and tear on machinery while maximizing safety and operational efficiency. Their adaptability in diverse environmental conditions—from bright lights to dark operations—makes them essential for ensuring consistent, high-quality outputs in various industrial settings.
Essential Features of Photoelectric Sensors
Photoelectric sensors are integral to the modern landscape of industrial automation. These devices detect objects by using a light beam, which can be adjusted to meet specific needs based on distance and the type of object being detected. Their design is straightforward yet sophisticated: a light source emits beams that are either interrupted or reflected by objects, triggering responses from the sensor. This core functionality enables a high degree of flexibility in how they’re applied across various fields.
The simplicity of these sensors belies their robust capabilities. They can operate over long distances unlike many other sensor types, and adjustments to the emitted light allow them to detect a wide range of object types. This versatility is what makes photoelectric sensors foundational in many automated processes.
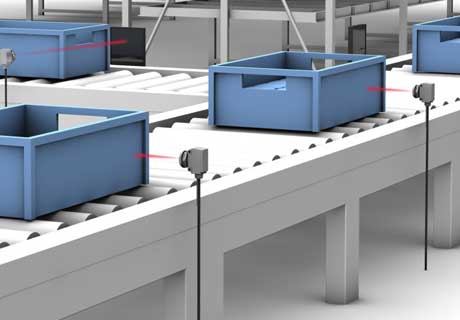
Efficiency and Speed Benefits
One of the main reasons industries lean heavily on photoelectric sensors is their contribution to enhanced efficiency and speed. These sensors provide real-time data that is critical in high-speed manufacturing environments, where they help streamline operations and reduce the likelihood of errors, which can be costly. By enabling faster response times and reliable operations, photoelectric sensors significantly boost productivity.
Their ability to quickly process changes in their environment makes them particularly valuable in sectors where timing is everything. From packaging to assembly lines, the precision of these sensors ensures that operations proceed smoothly and without interruption.
Non-Contact Detection: Advantages
The non-contact nature of photoelectric sensors presents several advantages over contact-based detection methods. Firstly, they minimize the risk of damage to both the sensors and the objects they detect, which is particularly important in industries dealing with delicate or expensive materials. Additionally, this feature significantly reduces wear and tear on the sensors themselves, leading to lower maintenance costs and longer operational lifespans.
Non-contact detection also allows for greater safety within the workplace. By eliminating the need to physically touch parts, these sensors help prevent accidents and enhance the overall safety of the production environment.
Wide Range of Applications
Omron Photoelectric sensors are used in a myriad of applications, demonstrating their adaptability. In manufacturing, they check for the presence or absence of components to ensure that products are assembled correctly. In logistics, they facilitate the sorting and tracking of packages. Their use in automotive safety systems, such as in adaptive cruise control and parking assistance, highlights their utility in non-industrial contexts as well.
This wide applicability is a testament to the sensor’s design and functionality, which can be tailored to meet the demands of various settings, from sterile clean rooms to rugged outdoor environments.
Environmental and Economic Benefits
Beyond their technical capabilities, photoelectric sensors also offer environmental and economic benefits. They are energy efficient, often requiring less power than other types of sensors. This efficiency contributes to reduced operational costs and supports sustainability initiatives within companies.
Economically, the longevity and low maintenance requirements of photoelectric sensors mean that investing in them can lead to significant cost savings over time. Environmentally, their precision and efficiency can help reduce waste materials, an important consideration in industries aiming to decrease their environmental footprint.
Conclusion
The widespread use of photoelectric sensors across various industries is a clear indication of their reliability and the vast array of benefits they offer. These sensors not only enhance operational efficiency and safety but also contribute to economic and environmental goals. As you start your career and learn to implement these technologies, understanding their full potential will enable you to make informed decisions that optimize productivity and sustainability. Photoelectric sensors are more than just components; they are vital tools that drive modern automation and safety.
